Every product has a life cycle from creation to disposal or recycling. It might surprise you that there is an entire dedicated part of that life cycle after a product is purchased. It is called reverse logistics.
Reverse logistics is a complex process involving various activities to improve customer service and manage returns. In this blog post, we’ll explain what reverse logistics in supply chain management is and how it affects the aftermarket of a product.
What is Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain Management?
Reverse logistics is a crucial aspect of supply chain management that involves the movement of products from the customer back to the seller or manufacturer.
This process is necessary for handling product returns and recycling. It begins at the end-user and moves backward through the supply chain to the manufacturer or distributor.
Reverse logistics can also involve end-users being responsible for the final product disposal, such as refurbishing, recycling, or resale. It plays a critical role in managing the flow of goods, reducing waste, and maximizing profits.
The 5Rs of Reverse Logistics
To effectively manage the flow of goods and reduce waste, understanding the 5Rs of reverse logistics is essential.
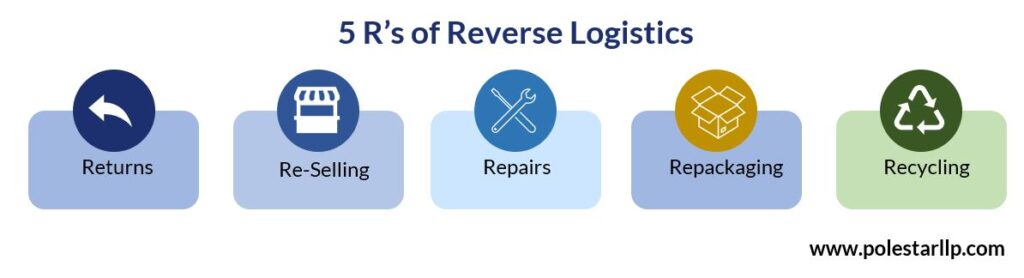
Returns
Efficient reverse logistics starts with returns, and it’s essential to have streamlined processes in place for receiving, inspecting, and testing returned products, whether in a B2C or B2B environment. This may involve:
- Utilizing a branded customer portal
- RMA initiation
- Reason codes
- Exchanges
- Shipping labels
- Check Status
- Automated customer notifications
- Validations,
- Approvals
- Supporting documentation
Recalls
Recalls are a more complex return format that often involves product defaults, potential hazards, government regulations, and liability concerns. Salvaging revenue after recalls can quickly help build brand trust.
Recycling
Sustainability is a critical concern in various industries, with electronic and tech sectors increasingly embracing recycling and reclamation efforts.
Companies should consider cost, seasonality, labor capacity, and other factors when addressing recycling opportunities while relying on RMS data to assess their sustainability efforts’ impact on operations.
Repackaging
Returned parts can be remanufactured or repaired inexpensively if no trouble is found during testing, and the same facility can also repack returns for resale using secondary channels like overstock.com.
Repair
If a product has minor faults, it can be repaired. An RMS can efficiently transfer repairable units to the proper level for multi-level depot repairs, ensuring efficient inventory processing and restocking with complete visibility.
These are just some activities necessary to manage returns and improve customer service.
How Reverse Logistics Works
Understanding how reverse logistics works is crucial to optimizing supply chain management and improving customer satisfaction.
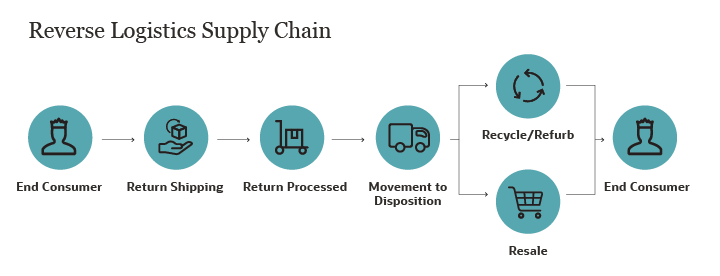
Processing Customer Returns
The return process starts with the customer’s desire to return a product. It involves authorization, assessing the product’s condition, planning for shipment, replacing defective items, and approving refunds.
Choosing a Return Strategy
Once a consumer returns a product to the manufacturer or distributor, the receiving entity plans the next steps, including inspecting the product and determining its disposition options, such as repair, resale, recycling, or refurbishment.
Moving Returned Products
Swiftly transferring the return to the appropriate department for reconditioning, repairing, or refurbishing is crucial in minimizing waste and turnover.
Repairing Returned Products
After a company reviews a returned product and chooses to repair it, the item is transferred to the repair center, while any valuable parts of an item that cannot be repaired may be salvaged and sold.
Recycling Returned Products
Reusing or reselling products or parts that cannot be repaired involves dispatching them to the recycling department.
The process might be complicated, but with proper reverse logistics planning, companies can improve their operations, reduce waste and increase profits.

Different Types of Aftermarket Logistics
There are different types of aftermarket logistics, each with its unique characteristics.
Returns Management
Efficient returns management is essential for enhancing customer loyalty and brand reputation, as it handles regular customer returns seamlessly.
Return Policy and Procedure
Consistency is key when it comes to customer return policies. Make sure to make them easily accessible to customers.
Remanufacturing or Refurbishment
By reconditioning returned products, organizations and retailers can avoid losing money on defective items and reduce waste.
Packaging Management
Organizations with efficient packaging management processes can reuse returned item packaging, saving costs and reducing waste.
Unsold products
The process of returning unsold products directly from end-users or fulfillment centers to manufacturers is often caused by delivery refusal, poor sales, or other reasons.
End of Service Life
Manufacturers must manage the proper environmental disposal of some products at the end of their useful life, requiring them to be returned.
Delivery Failure
Efficient organizations can manage delivery failure by correcting the issue and resending the product. Otherwise, it will be returned to fulfillment centers and shipped back to the manufacturer.
Rental Equipment
Rented or leased products are typically returned to the manufacturer for disposal, recycling, or redeployment at the end of the agreed-upon term.
Repair and Maintenance
Returns may involve repairs or warranty work for products like consumer electronics (such as laptops).
Understanding the various types of aftermarket logistics can help you enhance your operations and provide better customer service.

Benefits of Effective Aftermarket Supply Chain
An effective aftermarket supply chain can bring numerous benefits to businesses. Here are some of them:
- Refining processes for what happens to products after delivery helps retain customers and save money.
- Collecting product data from customer engagement provides insight into an organization’s supply chain and an opportunity to improve products and/or the customer experience.
- Optimized reverse logistics leads to better supply chain visibility, which leads to cost reduction, greater customer satisfaction, better customer retention, faster and better service, loss reduction, improved brand sentiment, waste reduction, and greater sustainability.
- A better understanding of customer returns and disposal processes can also lead to more strategic purchasing decisions, reducing waste.

Challenges of Reverse Logistics: Addressing Common Obstacles
The rise of e-commerce has led to a surge in product returns, causing significant challenges for companies to manage their reverse logistics. Some common obstacles include:
- Warehousing and storage costs
- Inconsistent returns management
- Lack of standardization
- Increased waste
However, purpose-built supply chain software for reverse logistics is now available for various industries, enabling more efficient, cost-effective, and customer-oriented processes.

Best Practices for a Sustainable and Efficient Reverse Logistics
To ensure a sustainable and efficient reverse logistics process, here are some best practices that businesses should consider:
Evaluate Relevant Policies and Agreements
Evaluate and update the processes regarding returns and repairs for our company. These protocols should be unambiguous and consider the underlying reasons for returns and repairs.
Collaborate with Suppliers
Collaborating closely with suppliers can result in a seamless and well-integrated experience for customers rather than a confusing one they may find challenging to navigate.
Utilize Data to Optimize Processes
Collecting data on product returns would help understand why customers are returning products. This information can then be used to adjust sales, product design, and forward logistics processes.
Implement Forward and Reverse Product Tracking
You can trace the ingredients by linking raw materials to the finished product and the customer order. This helps process recalls more efficiently as you can selectively identify the specific issue and issue recalls instead of recalling entire product lines.
Centralize Return Centers for Efficiency
Centralizing returns in one location allows for more efficient sorting and decision-making regarding product value. If a dedicated return center is not feasible, consider allocating space in your warehouse or factory for returns.
Analyze Logistics and Transportation Methods
Regularly review forward and reverse logistics and transportation processes to explore opportunities for integration. For instance, consider having delivery drivers collect empty pallets while dropping off full ones to save time, money, and trips.
Automate Processes for Enhanced Efficiency
Consider using cloud-based logistics software to make your operations more efficient. This type of software can assist in tracking asset recovery, managing refurbishment, and offering business intelligence analytics.
Implementing these best practices can help you develop a sustainable and efficient reverse logistics process, reducing the cost of returns and increasing the value recaptured from returned products.

Begin Optimizing Your Supply Chain Today by Partnering with Hopewell Logistics!
As mentioned, effective management of reverse logistics can enhance sustainability, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. For businesses looking to implement or improve their reverse logistics processes, a third-party logistics provider (3PL) can be a game-changer.
At Hopewell Logistics, we specialize in end-to-end solutions for managing the flow of returned goods. Contact us today or visit our website to learn more about how we can help enhance your reverse logistics process.





